
SSC CPO Exam Paper - 2017 "held on 01 July 2017" Shift-1
(General Knowledge and General Awareness)
QID : 51 - What is the full form of FDI?
Options:
1) Foreign Direct Input
2) Foreign Direct Investment
3) Fiscal Direct Investment
4) Fiscal Direct Input
Correct Answer: Foreign Direct Investment
QID : 52 - In which situation, wages and prices chase each other at a very
quick speed?
Options:
1) Disinflation
2) Reflation
3) Stagflation
4) Hyper-inflation
Correct Answer: Hyper-inflation
QID : 53 - Banking comes under which of the following sector?
Options:
1) Primary sector
2) Secondary sector
3) Tertiary sector
4) Both Secondary and Tertiary sectors
Correct Answer: Tertiary sector
QID : 54 - Which of the following is a basic characteristic of
'Oligopoly'?
Options:
1) Many sellers, many buyers
2) Few sellers, few buyers
3) Few sellers, many buyers
4) Many sellers, few buyers
Correct Answer: Few sellers, many buyers
QID : 55 - What was the main objective of the 5th Five Year Plan?
Options:
1) Removal of poverty and achievement of self-reliance
2) Faster, more inclusive and sustainable growth
3) Inclusive growth
4) None of these
Correct Answer: Removal of poverty and achievement of self-reliance
QID : 56 - _____ is a form of government in which the rulers are elected
by the people.
Options:
1) Autocratic
2) Monarchic
3) Democratic
4) Authoritarian
Correct Answer: Democratic
QID : 57 - Who said 'The God, who gave us life, gave us the liberty at the
same time'?
Options:
1) Marx
2) Plato
3) Jefferson
4) Locke
Correct Answer: Jefferson
QID : 58 - What is 'Patriarchic Society'?
Options:
1) System that values women more than men
2) System that values men more than women
3) System that values both men and women equally
4) System that values elders
Correct Answer: System that values men more than women
QID : 59 - Members of Rajya Sabha are elected for how many years?
Options:
1) Two years
2) Three years
3) Five years
4) Six years
Correct Answer: Six years
QID : 60 - Under which pardoning power of the President, duration of
sentence is reduced without changing its character?
Options:
1) Commutation
2) Remission
3) Respite
4) Reprieve
Correct Answer: Remission
QID : 61 - In Pocket Veto, the President of India can keep a bill for how
much duration?
Options:
1) 1 month
2) 6 months
3) 12 months
4) Indefinite period
Correct Answer: Indefinite period
QID : 62 - The President's seat can be left vacant for how much duration?
Options:
1) 6 Months
2) 3 Months
3) 9 Months
4) 12 Months
Correct Answer: 6 Months
QID : 63 - Which constitutional Amendment Act of India reduced voting age
from 21 years to 18 years?
Options:
1) 42nd Amendment Act
2) 61st Amendment Act
3) 74th Amendment Act
4) 83rd Amendment Act
Correct Answer: 61st Amendment Act
QID : 64 - In which year East India Company was ceased to work and India
was completely undertaken by British Govt.?
Options:
1) 1838
2) 1919
3) 1858
4) 1898
Correct Answer: 1858
QID : 65 - At which location, a sculptor of chariot of Harappan time was
found?
Options:
1) Lothal
2) Banawali
3) Daimabad
4) Kalibangan
Correct Answer: Daimabad
QID : 66 - First Satyagrah started from Champaran for opposing the
cultivation of ________.
Options:
1) Cotton
2) Indigo
3) Silk
4) Kesar
Correct Answer: Indigo
QID : 67 - Who was the founder of 'Vikramshila University'?
Options:
1) Vijay Sen
2) Atisa
3) Dharampal
4) Ballal Sen
Correct Answer: Dharampal
QID : 68 - When India got Independence, who was the Prime Minister of
England?
Options:
1) William Bentick
2) Warren Hasting
3) Margaret Thatcher
4) Climent Atlee
Correct Answer: Climent Atlee
QID : 69 -
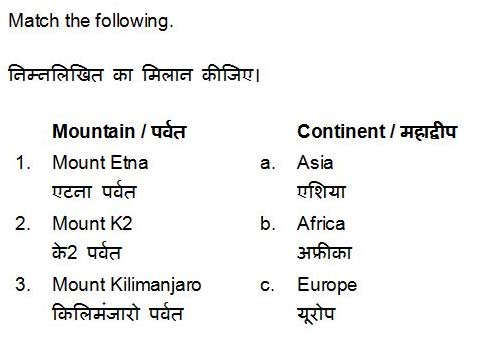
Options:
1) 1 – a, 2 – b, 3 – c
2) 1 – b, 2 – a, 3 – c
3) 1 – c, 2 – a, 3 – b
4) 1 – a, 2 – c, 3 – b
Correct Answer: 1 – c, 2 – a, 3 – b
QID : 70 - Which of the following mountain range separates Europe and
Asia?
Options:
1) Rocky Mountain Range
2) Himalayan Mountain Range
3) Ural Mountain Range
4) Appalachian Mountain Range
Correct Answer: Ural Mountain Range
QID : 71 - Suez Canel connects which of the following water bodies?
Options:
1) Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea
2) Mediterranean Sea and Red Sea
3) Pacific Ocean and Atlantic Ocean
4) Mediterranean Sea and Arctic Ocean
Correct Answer: Mediterranean Sea and Red Sea
QID : 72 - Which of the following Indian state does not share
International land border?
Options:
1) Jammu and Kashmir
2) Uttar Pradesh
3) Bihar
4) Madhya Pradesh
Correct Answer: Madhya Pradesh
QID : 73 - In which of the following city, world's second longest beach is
located?
Options:
1) Mumbai
2) Kolkata
3) Puducherry
4) Chennai
Correct Answer: Chennai
QID : 74 - Which of the following brings back deoxygenated blood from
different parts of human body to heart?
Options:
1) Veins
2) Arteries
3) Nerves
4) Lungs
Correct Answer: Veins
QID : 75 - Which of the following is a warm blooded animal?
Options:
1) Turtle
2) Snake
3) Ape
4) Lizard
Correct Answer: Ape
QID : 76 - Where is bile stored?
Options:
1) Liver
2) Kidney
3) Gall bladder
4) Spleen
Correct Answer: Gall bladder
QID : 77 - Which of the following is not a connective tissue?
Options:
1) Adipose Tissue
2) Compact Bone
3) Cardiac Muscle
4) Areolar Tissue
Correct Answer: Cardiac Muscle
QID : 78 - Normally how many times the human heart beats in a minute?
Options:
1) 82
2) 75
3) 72
4) 85
Correct Answer: 72
QID : 79 - Muscle fatigue occurs due to accumulation of ______.
Options:
1) ATP
2) ADP
3) Lactic Acid
4) Carbonic Acid
Correct Answer: Lactic Acid
QID : 80 - The inexhaustible source of energy of stars is due to _____.
Options:
1) Conversion of hydrogen to helium
2) Conversion of helium to hydrogen
3) Decay of radioactive elements
4) Excess of oxygen
Correct Answer: Conversion of hydrogen to helium
QID : 81 - Which of the following waves has the highest frequency?
Options:
1) Radio
2) Infrared
3) Microwaves
4) Gamma-rays
Correct Answer: Gamma-rays
QID : 82 - Why the clear nights are cooler than the cloudy nights?
Options:
1) Conductance
2) Condensation
3) Radiation
4) Insulation
Correct Answer: Radiation
QID : 83 - The subatomic particle that does not have any electric charge
is a/an _____.
Options:
1) Electron
2) Proton
3) Neutron
4) All options are correct.
Correct Answer: Neutron
QID : 84 - Dot-Matrix is an example of which of the following?
Options:
1) A software
2) Scanner
3) Printer
4) Keyboard
Correct Answer: Printer
QID : 85 - Which of the following pair is INCORRECT?
Options:
1) 10 MB – 10240 KB
2) 1 GB – 10240 MB
3) 1 TB – 1024 GB
4) 1 KB – 1024 Bytes
Correct Answer: 1 GB – 10240 MB
QID : 86 - Which of the following gas is used in bulb?
Options:
1) Hydrogen
2) Carbon-dioxide
3) Carbon-mono-oxide
4) Argon
Correct Answer: Argon
QID : 87 - Chlorine gas is a major component of which of the following?
Options:
1) Water
2) Tear gas
3) Liquefied Petroleum Gas
4) Gobar gas
Correct Answer: Tear gas
QID : 88 - What is Brine solution?
Options:
1) Excess salt + water
2) Silver
3) Excess Ethanol + water
4) Excess starch + water
Correct Answer: Excess salt + water
QID : 89 - pH scale ranges from _____ .
Options:
1) 1 to 14
2) 1 to 7
3) 0 to 14
4) 0 to 7
Correct Answer: 0 to 14
QID : 90 - Which of the following primarily causes lead pollution?
Options:
1) CFL Lamp
2) Automobile Battery
3) Polymer
4) Diesel Engine
Correct Answer: Automobile Battery
QID : 91 - What was the main aim of Montreal Protocol?
Options:
1) Protection of Ozone layer
2) Bio-diversity Conservation
3) Global Warming
4) Climate Change
Correct Answer: Protection of Ozone layer
QID : 92 - Supersonic jets cause thinning of which layer?
Options:
1) O2 layer
2) O3 layer
3) CO2 layer
4) SO2 layer
Correct Answer: O3 layer
QID : 93 - What is the name of the app launched by the Union Ministry of
Power to provide real time information sharing on power supply?
Options:
1) URJAMITRA
2) BHIM
3) URJA
4) UMANG
Correct Answer: URJAMITRA
QID : 94 - Who discovered 'Portland cement'?
Options:
1) Michael Faraday
2) Guglielmo Marconi
3) Joseph Aspdin
4) Isaac Newton
Correct Answer: Joseph Aspdin
QID : 95 - Nitin Thimmaiah is related to which sport?
Options:
1) Table Tennis
2) Boxing
3) Cricket
4) Hockey
Correct Answer: Hockey
QID : 96 -

Options:
1) 1-d, 2-c, 3-a, 4-b
2) 1-c, 2-d, 3-a, 4-b
3) 1-b, 2-a, 3-d, 4-c
4) 1-d, 2-a, 3-b, 4-c
Correct Answer: 1-d, 2-c, 3-a, 4-b
QID : 97 - Which Chief Minister has been awarded with the 'Transformative
Chief Minister Award' on May 8, 2017?
Options:
1) Yogi Adityanath, Uttar Pradesh
2) Chandrababu Naidu, Andhra Pradesh
3) Arvind Kejriwal, Delhi
4) Vasundhara Raje Scindia, Rajasthan
Correct Answer: Chandrababu Naidu, Andhra Pradesh
QID : 98 - Who wrote the book named 'Exile'?
Options:
1) Barkha Dutt
2) Valmik Thapar
3) Tasleema Nasreen
4) Ranbir Singh Sindhu
Correct Answer: Tasleema Nasreen
QID : 99 - Pakistan has leased Gwadar port to state-run firm of which
country for 40 years?
Options:
1) Iran
2) China
3) Afghanistan
4) India
Correct Answer: China
QID : 100 - Which neighbouring country of India is not among the founding
members of SAARC?
Options:
1) Nepal
2) Bangladesh
3) Afghanistan
4) Bhutan
Correct Answer: Afghanistan